10 Subcutaneous Injections For Easy Medication
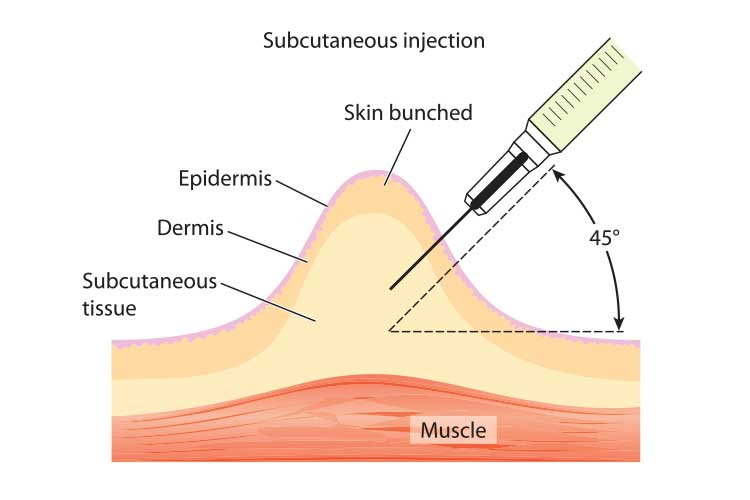
Subcutaneous injections have become a common method for administering medications, especially for patients who require regular doses of certain drugs. This technique involves injecting medication into the fatty tissue just beneath the skin, rather than into a muscle or vein. The subcutaneous route offers several advantages, including reduced pain, easier administration, and improved absorption rates for certain medications. Here, we will explore 10 subcutaneous injections used for various medical conditions, highlighting their applications, benefits, and administration guidelines.
Key Points
- Subcutaneous injections are used for a wide range of medications, including insulin, vaccines, and biologics.
- The technique involves injecting medication into the fatty tissue beneath the skin.
- Subcutaneous injections offer benefits such as reduced pain, easier administration, and improved absorption rates.
- Proper technique and site rotation are crucial for effective and safe administration.
- Patient education and training are essential for successful self-administration.
Common Subcutaneous Injections

Subcutaneous injections are utilized for various therapeutic purposes, including the management of chronic diseases, prevention of illnesses through vaccinations, and the treatment of acute conditions. The following are 10 examples of subcutaneous injections and their applications:
1. Insulin
Insulin is perhaps the most well-known medication administered via subcutaneous injection. It is crucial for the management of diabetes, helping to regulate blood glucose levels. There are several types of insulin, each with different onset and duration times, allowing for tailored treatment plans.
2. Epinephrine Auto-Injectors (EpiPen)
Epinephrine auto-injectors, such as the EpiPen, are used for the emergency treatment of severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis). These devices automatically inject a dose of epinephrine into the thigh when activated, providing rapid relief from symptoms.
3. Vaccines
Some vaccines, like the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine and certain flu vaccines, are administered subcutaneously. This route can help stimulate a strong immune response, providing protection against specific diseases.
4. Growth Hormone
Growth hormone injections are given subcutaneously to treat growth hormone deficiency in children and adults. This medication helps promote growth and development in children and can improve muscle mass and bone density in adults.
5. Fertility Medications
Medications used to stimulate ovulation or support fertility treatments, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), are often administered subcutaneously. These injections help regulate ovulation and improve the chances of conception.
6. Interferon Beta-1a (Rebif)
Used in the treatment of multiple sclerosis, interferon beta-1a is injected subcutaneously to reduce the frequency of relapses and slow the progression of the disease. It works by modifying the immune system’s response.
7. Enbrel (Etanercept)
Enbrel is a biologic medication used to treat autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and plaque psoriasis. It is administered subcutaneously, usually once or twice a week, to reduce inflammation and slow disease progression.
8. Humira (Adalimumab)
Humira is another biologic drug that is injected subcutaneously to treat various conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis. It helps reduce inflammation and prevent disease flare-ups.
9. Bydureon (Exenatide)
Bydureon is used in the management of type 2 diabetes. It is administered subcutaneously once a week and helps improve glycemic control, promote weight loss, and reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events.
10. Victoza (Liraglutide)
Victoza is also used for type 2 diabetes management and is given subcutaneously once a day. It improves blood sugar control, aids in weight loss, and has been shown to reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in adults with established cardiovascular disease.
| Medication | Frequency of Administration | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin | Varying, depending on type and patient needs | Hypoglycemia, injection site reactions |
| Epinephrine Auto-Injectors | As needed for anaphylaxis | Pallor, tremor, nervousness |
| Vaccines | According to vaccination schedule | Pain, redness, swelling at the injection site |
| Growth Hormone | Usually daily | Headache, fatigue, injection site reactions |
| Fertility Medications | Varying, based on treatment protocol | Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, abdominal pain |
| Interferon Beta-1a | 3 times a week | Flu-like symptoms, injection site reactions |
| Enbrel | Once or twice a week | Injection site reactions, upper respiratory infections |
| Humira | Every other week or weekly | Injection site reactions, upper respiratory infections |
| Bydureon | Once a week | Nausea, diarrhea, injection site reactions |
| Victoza | Once a day | Nausea, vomiting, injection site reactions |

In conclusion, subcutaneous injections play a vital role in the management of various medical conditions. Their ease of administration, reduced pain compared to intramuscular injections, and improved absorption rates make them a preferred method for many medications. However, proper technique, patient education, and adherence to administration guidelines are essential for the safe and effective use of subcutaneous injections.
What is the most common side effect of subcutaneous injections?
+Injection site reactions, such as redness, swelling, and pain, are among the most common side effects of subcutaneous injections. However, these reactions are usually mild and temporary.
How often should injection sites be rotated?
+Injection sites should be rotated regularly to prevent lipodystrophy, a condition characterized by the abnormal distribution of body fat. The specific rotation schedule may vary depending on the medication and the patient’s treatment plan.
Can subcutaneous injections be self-administered?
+Yes, many subcutaneous injections can be self-administered after proper training and education. Patients should follow the specific instructions provided by their healthcare provider and the medication’s manufacturer.
What are the benefits of subcutaneous injections over other administration routes?
+Subcutaneous injections offer several benefits, including reduced pain, easier administration, and improved absorption rates for certain medications. They also allow for more flexible dosing schedules and can be less invasive than intravenous or intramuscular injections.



