Ecg Lead Placement
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a fundamental diagnostic tool in cardiology, providing valuable insights into the heart's electrical activity. The accuracy of an ECG reading is heavily dependent on the correct placement of electrodes on the body. ECG lead placement is a critical aspect of obtaining a reliable and interpretable ECG tracing. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of ECG lead placement, exploring the standard positions, variations, and considerations for different patient populations.
Key Points
- The standard 12-lead ECG involves the placement of 10 electrodes on the chest and limbs to capture the heart's electrical activity from different angles.
- Correct electrode placement is crucial for accurate ECG interpretation, as misplacement can lead to incorrect diagnoses.
- Variations in lead placement may be necessary for specific patient populations, such as pediatric or obese patients.
- Understanding the electrical axis of the heart and the relationship between lead placement and ECG waveforms is essential for accurate interpretation.
- Technological advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated ECG systems, including wireless and mobile devices, which still require proper lead placement for accurate readings.
Standard ECG Lead Placement
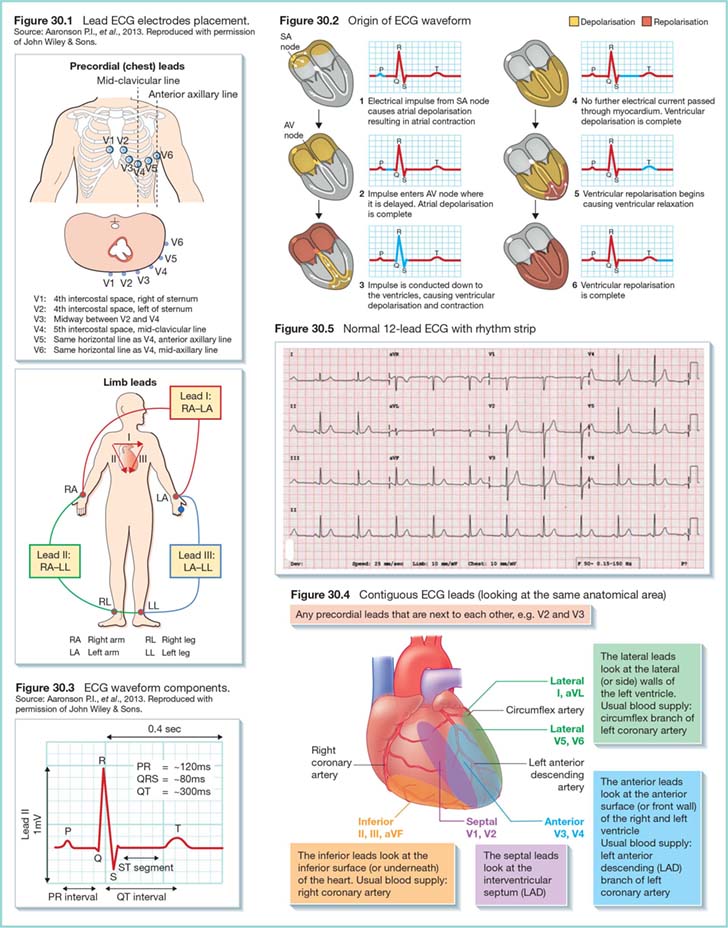
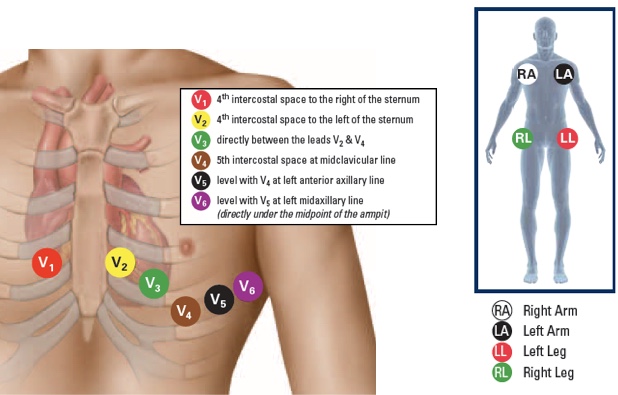
The standard 12-lead ECG is the most commonly used configuration, involving the placement of 10 electrodes on the body: 6 precordial (chest) leads and 4 limb leads. The limb leads are designated as RA (right arm), LA (left arm), RL (right leg), and LL (left leg), while the precordial leads are labeled V1 to V6. Each lead provides a unique view of the heart’s electrical activity, and together, they offer a comprehensive picture of cardiac function.
Precordial Lead Placement
Precordial leads are placed directly on the chest wall, with specific positions defined to capture the heart’s electrical activity from different angles. V1 and V2 are placed in the fourth intercostal space, to the right and left of the sternum, respectively. V3 is positioned midway between V2 and V4. V4 is located in the fifth intercostal space, in the midclavicular line. V5 and V6 are placed in the same horizontal plane as V4 but in the anterior axillary line and midaxillary line, respectively. The correct placement of these leads is vital for accurate detection of myocardial infarction, ischemia, and other cardiac conditions.
Limb Lead Placement
The limb leads are placed on the arms and legs, with the exact position influencing the ECG tracing. The right and left arm electrodes (RA and LA) are typically placed on the lateral aspect of the arm, just above the wrist. The right and left leg electrodes (RL and LL) are placed on the lateral aspect of the leg, just above the ankle. Correct placement of limb leads helps in reducing electrical interference and ensuring accurate ECG readings.
| Lead | Placement |
|---|---|
| V1 | Fourth intercostal space, right of sternum |
| V2 | Fourth intercostal space, left of sternum |
| V3 | Midway between V2 and V4 |
| V4 | Fifth intercostal space, midclavicular line |
| V5 | Anterior axillary line, same plane as V4 |
| V6 | Midaxillary line, same plane as V4 |
| RA | Lateral aspect of right arm, above wrist |
| LA | Lateral aspect of left arm, above wrist |
| RL | Lateral aspect of right leg, above ankle |
| LL | Lateral aspect of left leg, above ankle |
Variations in ECG Lead Placement

While the standard 12-lead ECG is widely used, variations in lead placement may be necessary for specific patient populations. For example, in pediatric patients, the precordial leads may need to be placed in different positions due to the smaller size of the chest. Similarly, in obese patients, the use of additional electrodes or alternative lead placements may be required to obtain accurate ECG readings.
Pediatric ECG Lead Placement
In pediatric patients, the precordial leads are often placed in slightly different positions due to the smaller chest size. V1 and V2 may be placed in the third intercostal space, while V4 may be placed in the fourth intercostal space. Understanding these variations is essential for accurate ECG interpretation in children and adolescents.
ECG Lead Placement in Obese Patients
In obese patients, the standard lead placement may not provide accurate ECG readings due to the increased distance between the heart and the electrodes. In such cases, additional electrodes or alternative lead placements may be used to improve the quality of the ECG tracing. This may include the use of posterior leads or the placement of electrodes in different positions on the chest wall.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, ECG lead placement is a critical aspect of obtaining accurate and reliable ECG readings. Understanding the standard positions, variations, and considerations for different patient populations is essential for healthcare professionals. As technology continues to evolve, the development of more sophisticated ECG systems, including wireless and mobile devices, will require ongoing education and training on proper lead placement to ensure accurate diagnoses and effective patient care.
What is the most common cause of inaccurate ECG readings?
+The most common cause of inaccurate ECG readings is incorrect electrode placement. This can lead to misinterpretation of the ECG tracing and incorrect diagnoses.
How do I ensure accurate ECG lead placement in pediatric patients?
+To ensure accurate ECG lead placement in pediatric patients, it is essential to understand the variations in lead placement required for smaller chest sizes. This may include placing V1 and V2 in the third intercostal space and V4 in the fourth intercostal space.
What are the implications of incorrect ECG lead placement in obese patients?
+Incorrect ECG lead placement in obese patients can lead to inaccurate ECG readings, which can result in misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment. It is essential to use additional electrodes or alternative lead placements to improve the quality of the ECG tracing in these patients.



