Encephalopathy Care: Comprehensive Treatment Options
Encephalopathy, a term that encompasses a range of brain disorders characterized by brain disease, damage, or malfunction, requires comprehensive and nuanced care to manage its multifaceted symptoms and complications. This neurological condition can result from various factors, including infections, toxins, metabolic disorders, and systemic diseases, each necessitating a tailored approach to treatment. As a neurologist with extensive experience in managing complex neurological cases, it's evident that a patient-centric, multidisciplinary strategy is essential for optimizing outcomes in encephalopathy care.
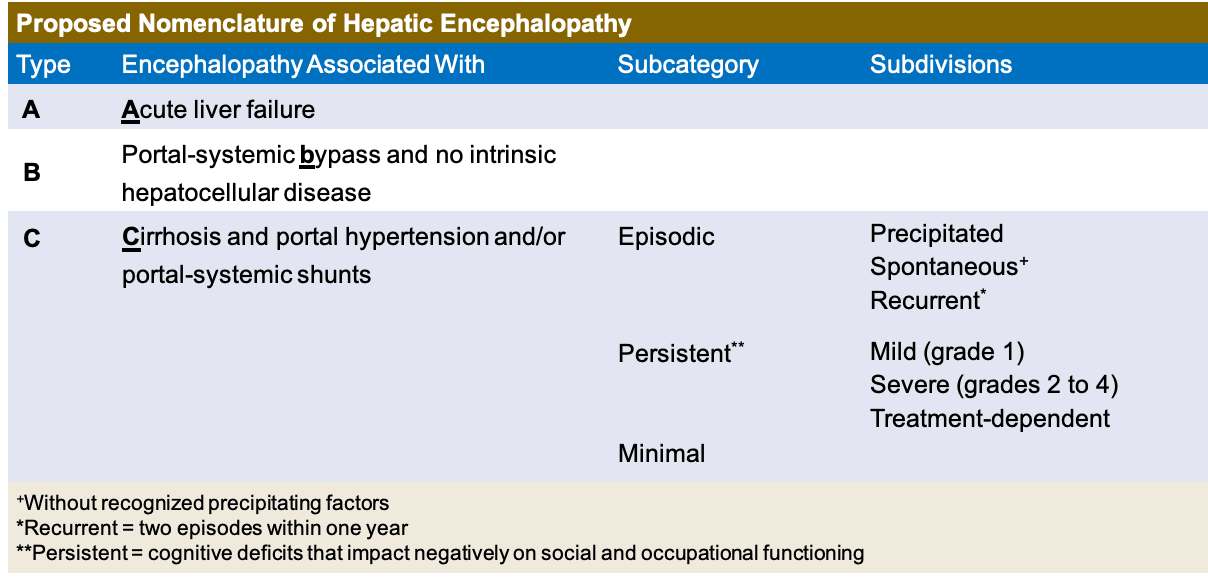
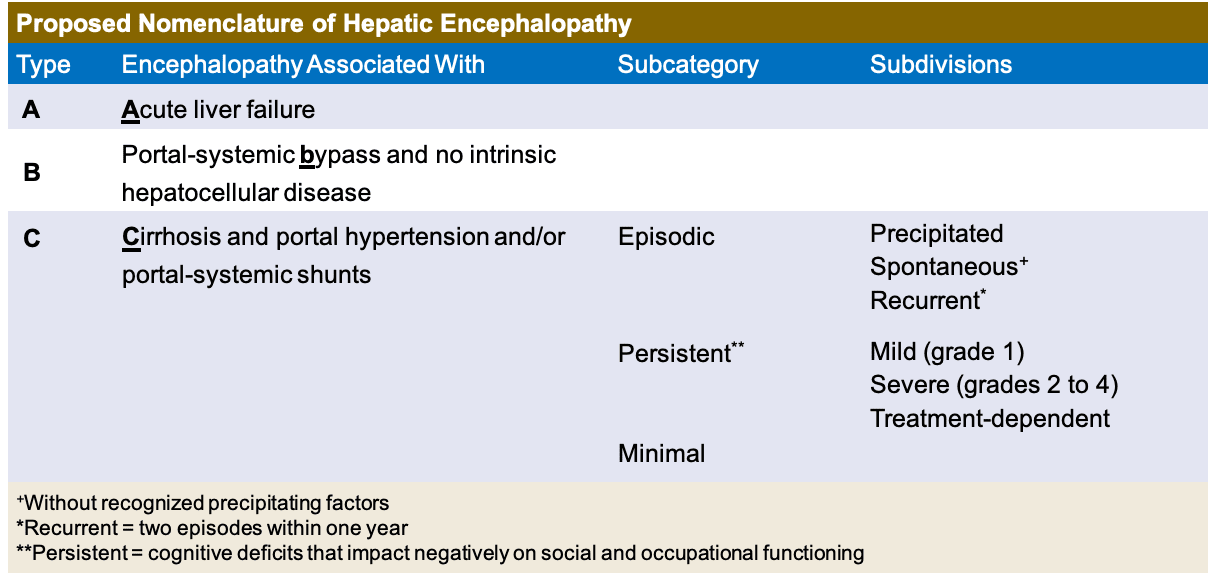
The complexity of encephalopathy necessitates a thorough diagnostic process to identify underlying causes and assess the extent of brain involvement. Advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, along with electroencephalography (EEG) and laboratory tests, play a crucial role in this diagnostic journey. Each diagnostic tool provides valuable insights into the nature of the condition, guiding healthcare providers towards the most appropriate treatment strategies. For instance, in cases of infectious encephalitis, timely identification of the causative pathogen is critical for initiating specific antimicrobial therapy. Similarly, in metabolic encephalopathies, correcting underlying biochemical imbalances is paramount for reversing neurological symptoms.
Key Points
- Comprehensive diagnostic evaluation is essential for identifying the underlying cause of encephalopathy.
- Treatment strategies must be tailored to the specific etiology and severity of the condition.
- A multidisciplinary care approach, involving neurologists, psychologists, rehabilitation specialists, and social workers, is crucial for managing encephalopathy.
- Supportive care measures, including seizure control, management of agitation and confusion, and prevention of complications, are vital components of encephalopathy care.
- Emerging therapies, such as immunomodulatory treatments and neuroprotective agents, offer promise for improving outcomes in select cases of encephalopathy.
Supportive Care and Management

Supportive care forms the backbone of encephalopathy management, focusing on alleviating symptoms, preventing complications, and enhancing the patient’s quality of life. Seizure control, for example, is a critical aspect of care, as seizures can exacerbate brain injury and worsen prognosis. The choice of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) depends on the type and frequency of seizures, as well as the patient’s overall clinical condition. Additionally, managing agitation, confusion, and other behavioral disturbances is essential, often requiring a combination of environmental modifications, behavioral therapies, and pharmacological interventions.
Pharmacological Interventions
Pharmacological interventions are tailored to the specific symptoms and underlying causes of encephalopathy. For instance, in cases of autoimmune encephalitis, immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory therapies may be indicated to reduce inflammation and halt disease progression. In contrast, metabolic encephalopathies may require targeted therapies to correct underlying biochemical abnormalities. The use of sedatives and antipsychotics for managing agitation and confusion must be carefully considered, weighing the benefits against the potential risks of exacerbating cognitive impairment or precipitating adverse effects.
| Category of Encephalopathy | Treatment Approach |
|---|---|
| Infectious Encephalitis | Antimicrobial therapy (antiviral, antibacterial, or antifungal) based on causative pathogen |
| Autoimmune Encephalitis | Immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory therapies (corticosteroids, IVIG, plasmapheresis) |
| Metabolic Encephalopathy | Correction of underlying biochemical imbalances (e.g., hypoglycemia, hyperammonemia) |
Rehabilitation and Recovery

Rehabilitation plays a pivotal role in the recovery process of patients with encephalopathy, focusing on regaining lost cognitive and physical functions. A multidisciplinary rehabilitation team, comprising physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, and psychologists, works together to design personalized rehabilitation plans. These plans are tailored to the patient’s specific needs and goals, aiming to maximize functional independence, reduce disability, and promote reintegration into community and social activities.
Cognitive rehabilitation, in particular, addresses the cognitive impairments common in encephalopathy, such as memory loss, attention deficits, and executive dysfunction. Compensatory strategies, cognitive training programs, and environmental adaptations can significantly improve cognitive function and overall quality of life. Furthermore, psychological support and counseling are essential for addressing the emotional and psychological challenges faced by patients and their families, including anxiety, depression, and coping with chronic illness.
Palliative Care Considerations
In cases where encephalopathy progresses to a advanced stage or becomes refractory to treatment, palliative care assumes a critical role. The focus shifts from curative interventions to providing comfort, alleviating suffering, and supporting the patient and their loved ones through the disease trajectory. Palliative care teams work closely with patients, families, and healthcare providers to address physical symptoms, emotional distress, and spiritual needs, ensuring a compassionate and dignified approach to care.
What are the common causes of encephalopathy?
+Encephalopathy can result from a variety of causes, including infections (viral, bacterial, fungal), metabolic disorders (hepatic encephalopathy, hypoglycemia), toxins (drug intoxication, environmental toxins), and systemic diseases (autoimmune disorders, cancer).
How is encephalopathy diagnosed?
+Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests (blood work, cerebrospinal fluid analysis), and imaging studies (MRI, CT scans), along with electroencephalography (EEG) to assess brain activity.
What are the treatment options for encephalopathy?
+Treatment is tailored to the underlying cause and severity of the condition, and may include antimicrobial therapy, immunosuppressive treatments, correction of biochemical abnormalities, supportive care measures, and rehabilitation therapies.
In conclusion, the care of patients with encephalopathy requires a comprehensive, patient-centric approach that integrates diagnostic precision, tailored treatment strategies, supportive care, rehabilitation, and palliative care considerations. By fostering a deep understanding of the complex interplay between the underlying causes, clinical manifestations, and therapeutic options, healthcare providers can optimize outcomes and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by this multifaceted condition. Ongoing research and clinical advancements hold promise for enhancing our ability to diagnose, treat, and manage encephalopathy, underscoring the importance of staying at the forefront of medical knowledge and practice.



