Ethnicity Vs Race: Know Your Identity
The terms "ethnicity" and "race" are often used interchangeably in everyday conversation, but they have distinct meanings in the context of social sciences and identity studies. Understanding the difference between these two concepts is essential for navigating the complexities of identity, culture, and social dynamics. In this article, we will delve into the nuances of ethnicity and race, exploring their definitions, historical context, and implications for individual and collective identity.
Key Points
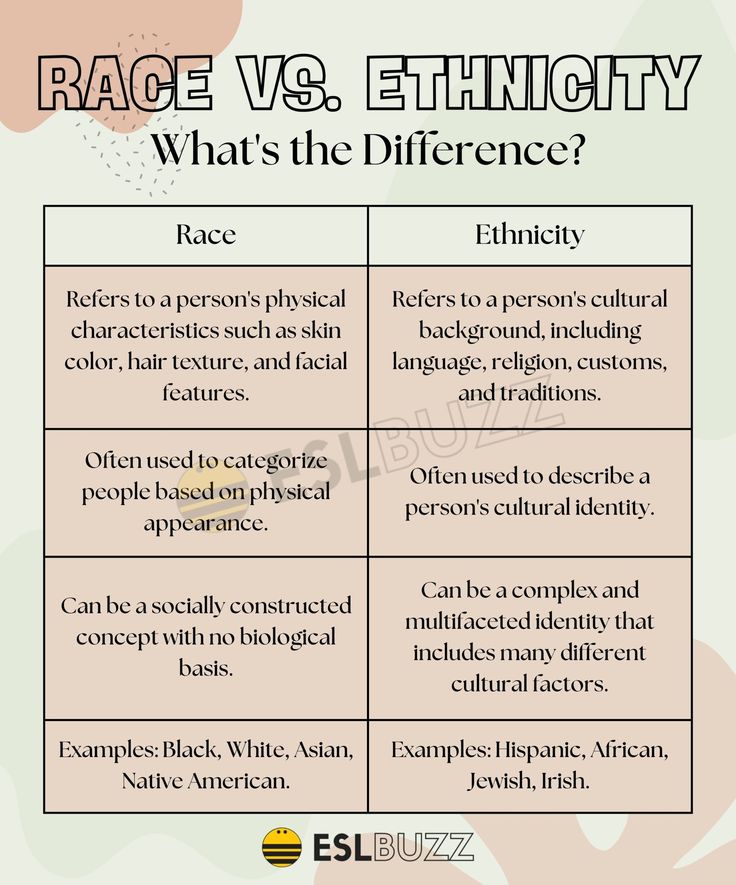
- Ethnicity refers to a group's shared cultural, linguistic, and historical heritage, while race is a socially constructed category based on physical characteristics.
- The distinction between ethnicity and race is crucial for understanding the complexities of identity and addressing social inequalities.
- Ethnicity is a fluid and dynamic concept, influenced by factors such as migration, assimilation, and cultural exchange.
- Race is a powerful social construct that has been used to justify discrimination, marginalization, and oppression throughout history.
- Recognizing and respecting the diversity of ethnic and racial identities is essential for promoting social justice, equality, and inclusivity.
Defining Ethnicity and Race

Ethnicity is a multifaceted concept that encompasses a group’s shared cultural, linguistic, and historical heritage. It is often tied to a specific geographic region, nationality, or ancestry. For example, a person may identify as Hispanic, African American, or Asian American, reflecting their cultural and ancestral roots. Ethnicity is not fixed and can evolve over time through processes such as migration, assimilation, and cultural exchange.
Race, on the other hand, is a socially constructed category based on physical characteristics such as skin color, hair texture, and facial features. The concept of race has been used to categorize and distinguish between different groups of people, often with profound social, economic, and political implications. The idea of race has been debunked as a scientifically valid concept, as it is not supported by genetic or biological evidence. Instead, it is a product of social, cultural, and historical forces that have shaped our understanding of human difference.
The Historical Context of Ethnicity and Race
The distinction between ethnicity and race is not new, but it has evolved over time. In the past, the term “race” was often used to refer to what we now understand as ethnicity. For example, the concept of “race” was used to distinguish between different European ethnic groups, such as the English, French, and German. However, with the advent of colonialism and the transatlantic slave trade, the concept of race took on a more sinister tone, with certain groups being deemed superior or inferior based on their physical characteristics.
The modern concept of race emerged in the 18th and 19th centuries, with the development of scientific racism and the idea of a racial hierarchy. This ideology posited that certain groups were inherently superior or inferior based on their biological characteristics, leading to the justification of slavery, colonialism, and segregation. The legacy of this ideology continues to shape our understanding of race and ethnicity today, with many people still experiencing discrimination, marginalization, and oppression based on their racial or ethnic identity.
| Category | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Ethnicity | A group's shared cultural, linguistic, and historical heritage | Hispanic, African American, Asian American |
| Race | A socially constructed category based on physical characteristics | Black, White, Asian, Indigenous |

The Implications of Ethnicity and Race

The distinction between ethnicity and race has significant implications for individual and collective identity. Ethnicity can provide a sense of belonging, cultural heritage, and community, while race can be a source of discrimination, marginalization, and oppression. Understanding the difference between these two concepts can help us navigate the complexities of identity and address the social inequalities that arise from racial and ethnic differences.
Moreover, recognizing the diversity of ethnic and racial identities is essential for promoting social justice, equality, and inclusivity. By acknowledging and respecting the differences between various ethnic and racial groups, we can work towards creating a more equitable and just society. This requires a nuanced understanding of the historical, cultural, and social contexts that shape our understanding of ethnicity and race.
Addressing Social Inequalities
Addressing social inequalities requires a multifaceted approach that takes into account the complexities of ethnicity and race. This involves recognizing the ways in which racial and ethnic differences are constructed and perpetuated, as well as the ways in which they intersect with other forms of identity, such as gender, class, and sexuality.
It also requires a commitment to promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion, through policies and practices that address the systemic inequalities faced by marginalized groups. This can involve initiatives such as affirmative action, cultural competency training, and community-based programs that promote social justice and equality.
What is the difference between ethnicity and race?
+Ethnicity refers to a group's shared cultural, linguistic, and historical heritage, while race is a socially constructed category based on physical characteristics.
Why is it important to recognize the distinction between ethnicity and race?
+Recognizing the distinction between ethnicity and race is crucial for understanding the complexities of identity and addressing social inequalities.
How can we promote social justice, equality, and inclusivity in relation to ethnicity and race?
+Promoting social justice, equality, and inclusivity requires a nuanced understanding of the historical, cultural, and social contexts that shape our understanding of ethnicity and race, as well as a commitment to addressing the systemic inequalities faced by marginalized groups.
In conclusion, the distinction between ethnicity and race is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires a nuanced understanding of the historical, cultural, and social contexts that shape our understanding of identity. By recognizing the fluidity and diversity of ethnic and racial identities, we can work towards promoting social justice, equality, and inclusivity, and creating a more equitable and just society for all.



