Flomax Uses

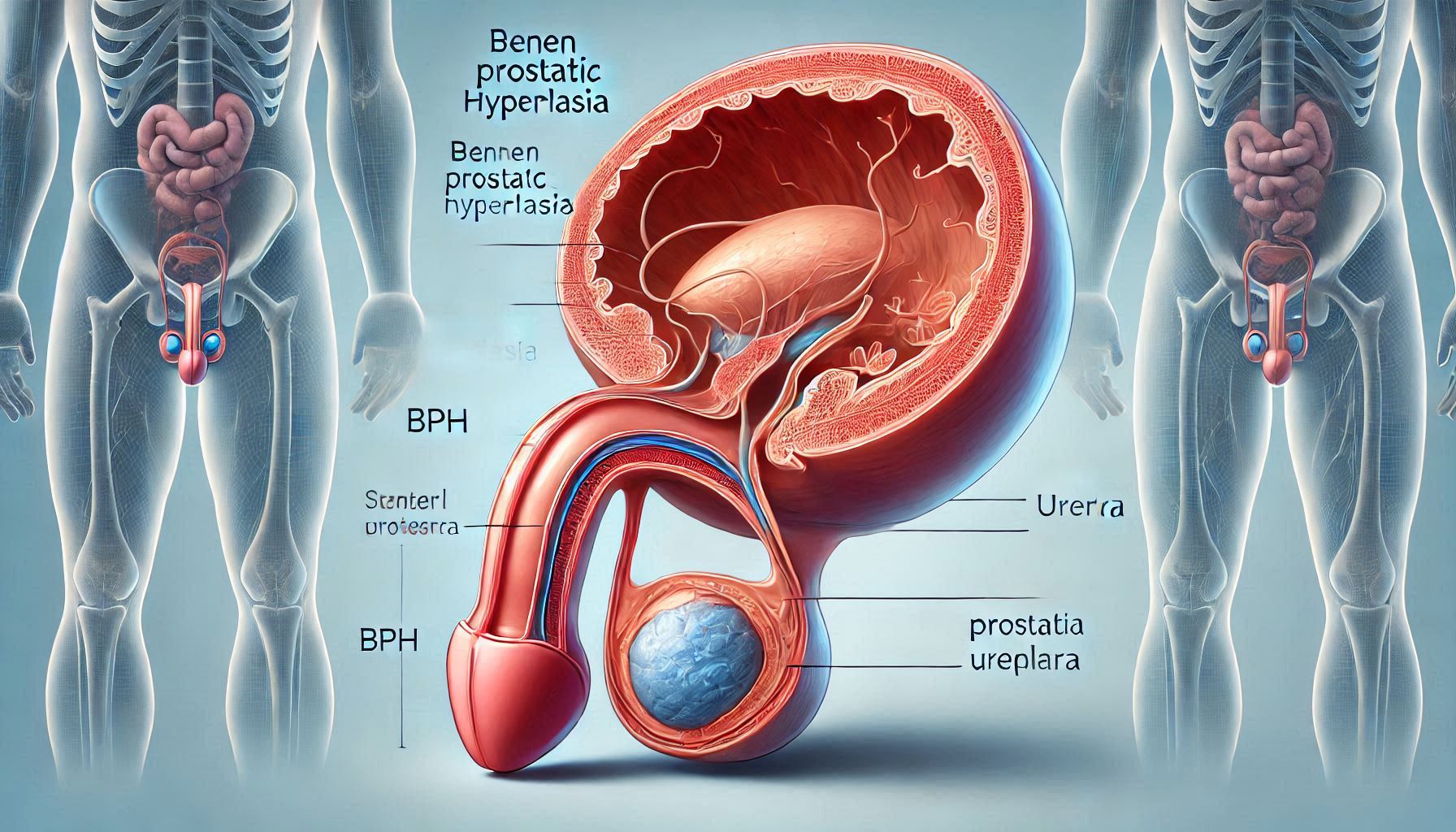
Flomax, also known by its generic name tamsulosin, is a medication primarily used to treat the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a condition in which the prostate gland is enlarged and can cause urinary symptoms. The prostate gland is a small, walnut-sized structure that is part of the male reproductive system, and its enlargement can lead to various urinary problems, including difficulty starting urination, weak urine flow, frequent urination, and the need to urinate multiple times during the night. Flomax works by relaxing the muscles in the prostate and the bladder neck, making it easier to urinate.
The drug belongs to a class of medications known as alpha-blockers, which work by blocking the action of certain natural chemicals in the body that cause the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck to tighten. By relaxing these muscles, Flomax helps to improve urine flow and reduce the symptoms of BPH. It does not shrink the size of the prostate but rather helps to alleviate the symptoms caused by its enlargement. Flomax is taken orally, usually once a day, and its effects can be noticeable within a few weeks of starting treatment, though it may take up to six weeks to experience the full benefits.
Key Points
- Flomax (tamsulosin) is used to treat symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), such as difficulty urinating and frequent urination.
- It works by relaxing the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck to improve urine flow.
- Flomax is an alpha-blocker and does not reduce the size of the prostate but alleviates symptoms caused by its enlargement.
- The medication is taken once daily and can start showing effects within a few weeks, with full benefits experienced within six weeks.
- Common side effects include dizziness, lightheadedness, and ejaculatory problems, but Flomax is generally well-tolerated.
How Flomax Works

Flomax’s mechanism of action involves the selective blockade of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, which are found in the smooth muscle of the prostate and bladder neck. By blocking these receptors, tamsulosin reduces the contraction of these muscles, thereby increasing the diameter of the urethra and improving urine flow. This selective action minimizes the impact on blood pressure, which is a common side effect of non-selective alpha-blockers. The selectivity of Flomax for the alpha-1A and alpha-1D receptor subtypes, which are predominantly found in the prostate, contributes to its effectiveness in treating BPH symptoms while minimizing effects on blood pressure.
Efficacy and Safety
Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of Flomax in improving the symptoms of BPH. Studies have shown significant improvements in urinary flow rates and reductions in symptoms such as hesitancy, weak stream, and nocturia (waking up at night to urinate). The safety profile of Flomax is generally favorable, with the most common side effects including dizziness, lightheadedness, and ejaculatory problems like retrograde ejaculation, where semen enters the bladder instead of exiting through the penis during ejaculation. Despite these side effects, Flomax is considered well-tolerated by most patients, and its benefits often outweigh the risks for men suffering from BPH symptoms.
| Common Side Effects | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Dizziness | Up to 10% |
| Lightheadedness | Up to 10% |
| Retrograde Ejaculation | Up to 18% |

Considerations and Precautions
While Flomax is effective in managing BPH symptoms, its use requires consideration of several factors. Patients should be cautioned about the potential for orthostatic hypotension (a sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing), especially during the initial dose period. This risk can be minimized by taking the first dose at bedtime and by gradually increasing the dose under medical supervision. Furthermore, Flomax can affect the pupil dilation during cataract surgery, a condition known as intraoperative floppy iris syndrome (IFIS), and ophthalmologists should be informed if the patient is taking or has taken Flomax.
Patient Selection and Monitoring
The selection of patients for Flomax treatment involves assessing the severity of BPH symptoms and evaluating the patient’s overall health status. Regular monitoring is essential to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and to manage any side effects that may arise. Patients should be educated on the proper use of the medication, the potential side effects, and the importance of follow-up appointments to adjust the treatment plan as needed.
What is the primary use of Flomax?
+Flomax is primarily used to treat the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), such as difficulty starting urination, weak urine flow, frequent urination, and nocturia.
How long does it take to experience the full benefits of Flomax?
+The full benefits of Flomax can be experienced within six weeks of starting treatment, though some improvements can be noticed within a few weeks.
Are there any precautions to consider when taking Flomax?
+Yes, precautions include the risk of orthostatic hypotension, potential effects on cataract surgery, and the importance of informing healthcare providers about all medications being taken to avoid drug interactions.
In conclusion, Flomax is a valuable treatment option for men suffering from the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Its efficacy in improving urinary flow and reducing BPH symptoms, combined with its generally favorable safety profile, make it a commonly prescribed medication for this condition. However, as with any medication, its use should be carefully considered and monitored by healthcare professionals to ensure the best outcomes for patients.



