Is Croup Contagious

Croup is a common childhood illness that affects the respiratory system, causing a distinctive barking cough and difficulty breathing. One of the primary concerns for parents and caregivers is whether croup is contagious. The answer to this question lies in understanding the underlying causes of croup and how it spreads.
Croup is typically caused by a viral infection, with the parainfluenza virus being the most common culprit. This virus is highly contagious and can spread from person to person through respiratory droplets, such as those produced by coughing or sneezing. When an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes, they release droplets into the air that can be inhaled by others, potentially leading to infection. Additionally, the virus can survive on surfaces for a period, allowing it to spread through touch.
Key Points
- Croup is primarily caused by a viral infection, most commonly the parainfluenza virus.
- The virus is highly contagious and can spread through respiratory droplets and contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Children under the age of 5 are most susceptible to croup due to their smaller airways and developing immune systems.
- Preventive measures such as frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and keeping surfaces clean can help reduce the risk of transmission.
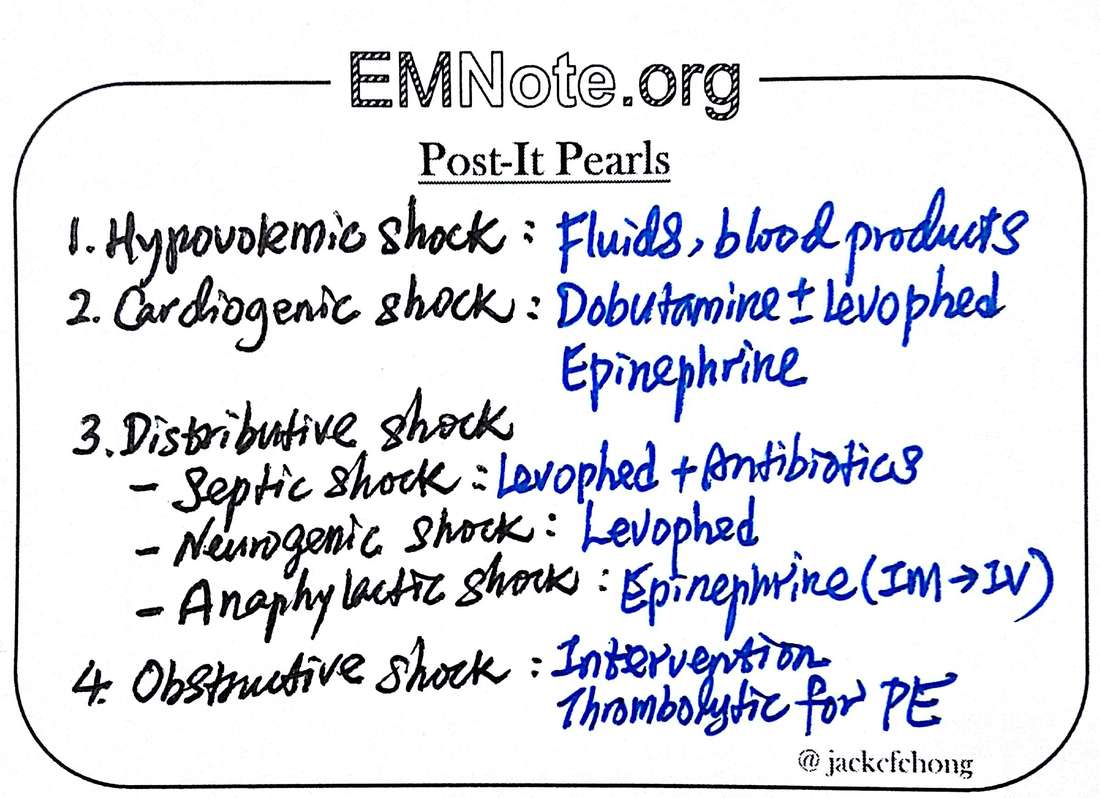
- Treatment for croup focuses on relieving symptoms and may include glucocorticoids, epinephrine, and supportive care such as ensuring adequate hydration and rest.
Understanding the Transmission of Croup

The transmission of croup can occur in various settings, including homes, schools, and daycare centers. Children under the age of 5 are particularly susceptible due to their smaller airways and developing immune systems. When a child with croup coughs or sneezes, they can spread the virus to others nearby. Moreover, touching surfaces contaminated with the virus and then touching one’s face can also lead to infection.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing the spread of croup involves a combination of good hygiene practices and avoiding close contact with infected individuals. Frequent handwashing with soap and water is crucial, especially after coming into contact with someone who has croup. Keeping surfaces clean and disinfected, particularly in areas where the infected child has been, can also help reduce the risk of transmission. Avoiding close contact with anyone who has croup, covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and ensuring that children are up to date on their vaccinations can also contribute to preventing the spread of the virus.
| Preventive Measure | Efficacy |
|---|---|
| Frequent Handwashing | Highly Effective |
| Avoiding Close Contact | Very Effective |
| Keeping Surfaces Clean | Effective |
| Vaccinations | Effective for Related Viruses |
Treatment and Management

The treatment of croup focuses on relieving symptoms and supporting the child’s recovery. Glucocorticoids, such as dexamethasone, are commonly used to reduce inflammation in the airways, while epinephrine may be administered in more severe cases to help open up the airways. Additionally, supportive care such as ensuring the child stays hydrated, gets plenty of rest, and is kept in a comfortable environment is crucial. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide oxygen therapy and close monitoring.
Complications and Long-Term Effects
While croup is generally a self-limiting condition, there can be complications, especially if the child has underlying health issues or if the infection is severe. Potential complications include respiratory failure, pneumonia, and bacterial tracheitis. It’s also worth noting that repeated episodes of croup can occur, particularly if the child is exposed to the virus again or has an underlying condition that predisposes them to respiratory infections.
How long is someone with croup contagious?
+Individuals with croup are typically contagious for 2-4 days after the onset of symptoms, but this can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the individual's immune response.
Can adults get croup?
+While croup is more common in children, adults can also contract the virus, especially if their immune system is compromised or they are exposed to someone with a severe infection.
How can I prevent my child from getting croup?
+Preventing croup involves practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with anyone who has croup, and keeping your child up to date on their vaccinations. Additionally, teaching your child to cover their mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing and to wash their hands regularly can help reduce the risk of transmission.
In conclusion, understanding that croup is contagious and knowing how it spreads is crucial for preventing its transmission and managing the condition effectively. By practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and being aware of the signs and symptoms of croup, parents and caregivers can help protect their children and support their recovery if they do become infected.



