Left Ventricle Health: Comprehensive Overview

The left ventricle, one of the four chambers of the heart, plays a crucial role in maintaining cardiovascular health. As the primary pumping chamber, it is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs to the rest of the body. Maintaining left ventricle health is essential to prevent various cardiovascular diseases and ensure overall well-being. In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the anatomy and physiology of the left ventricle, explore the risk factors and symptoms of left ventricle-related diseases, and discuss the diagnostic methods and treatment options available.
Key Points
- The left ventricle is the primary pumping chamber of the heart, responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
- Left ventricle health is crucial to prevent cardiovascular diseases such as heart failure, coronary artery disease, and cardiomyopathy.
- Risk factors for left ventricle-related diseases include hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking, and family history.
- Symptoms of left ventricle-related diseases may include shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and swelling in the legs and feet.
- Diagnostic methods for left ventricle-related diseases include echocardiogram, cardiac catheterization, and cardiac MRI.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Left Ventricle
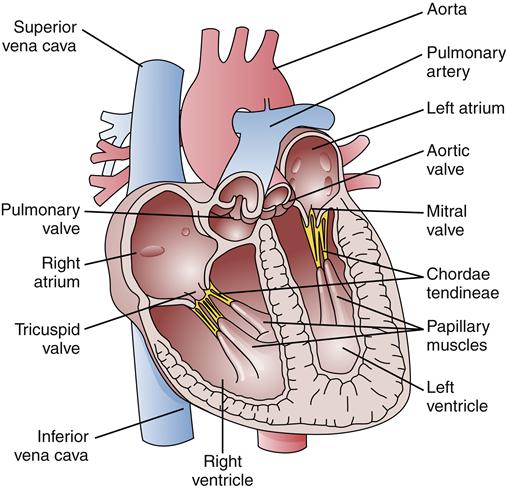
The left ventricle is a muscular chamber located in the lower left side of the heart. It receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through the pulmonary veins and pumps it out to the rest of the body through the aorta, the largest artery in the body. The left ventricle has a thick muscular wall, known as the myocardium, which contracts and relaxes to pump blood. The left ventricle also has a unique structure, with a mitral valve that separates it from the left atrium and an aortic valve that separates it from the aorta.
The left ventricle plays a critical role in maintaining blood pressure and ensuring that the body receives the oxygen and nutrients it needs. It pumps approximately 2,000 gallons of blood per day, with a pressure of around 120⁄80 mmHg. The left ventricle is also responsible for regulating blood flow to the brain, kidneys, and other vital organs.
Risk Factors for Left Ventricle-Related Diseases
Several risk factors can contribute to the development of left ventricle-related diseases, including: hypertension, which can cause the left ventricle to work harder and become thicker, leading to reduced function and increased risk of heart failure. Diabetes, which can damage the blood vessels and nerves that control the heart, leading to reduced left ventricle function and increased risk of heart disease. High cholesterol, which can cause the buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart and increased risk of coronary artery disease. Smoking, which can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease. Family history, which can increase the risk of left ventricle-related diseases due to genetic factors.| Risk Factor | Relative Risk |
|---|---|
| Hypertension | 2.5 |
| Diabetes | 2.0 |
| High Cholesterol | 1.8 |
| Smoking | 1.5 |
| Family History | 1.2 |

Symptoms of Left Ventricle-Related Diseases
Symptoms of left ventricle-related diseases may vary depending on the underlying condition, but common symptoms include: shortness of breath, which can occur when the left ventricle is not pumping enough blood to meet the body’s needs. Fatigue, which can occur when the left ventricle is not pumping enough blood to the muscles and other tissues. Chest pain, which can occur when the heart is not receiving enough blood flow. Swelling in the legs and feet, which can occur when the left ventricle is not pumping enough blood to the kidneys, leading to fluid buildup.
Diagnostic Methods for Left Ventricle-Related Diseases
Several diagnostic methods are available to diagnose left ventricle-related diseases, including: echocardiogram, which uses sound waves to create images of the heart and evaluate left ventricle function. Cardiac catheterization, which involves inserting a catheter into the heart to measure blood pressure and flow. Cardiac MRI, which uses magnetic resonance imaging to create detailed images of the heart and evaluate left ventricle function.Treatment Options for Left Ventricle-Related Diseases
Treatment options for left ventricle-related diseases depend on the underlying condition and may include: medications, such as beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, and diuretics, to manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction, to manage risk factors and improve overall health. Surgery, such as coronary artery bypass grafting or heart transplantation, to treat underlying conditions and improve left ventricle function.What are the most common causes of left ventricle-related diseases?
+The most common causes of left ventricle-related diseases include hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking, and family history.
How can I prevent left ventricle-related diseases?
+You can prevent left ventricle-related diseases by managing risk factors, such as maintaining a healthy blood pressure, controlling diabetes, and avoiding smoking.
What are the symptoms of left ventricle-related diseases?
+Symptoms of left ventricle-related diseases may include shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and swelling in the legs and feet.
In conclusion, maintaining left ventricle health is crucial to prevent cardiovascular diseases and ensure overall well-being. By understanding the anatomy and physiology of the left ventricle, recognizing risk factors and symptoms, and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their heart health. As research continues to advance, new diagnostic methods and treatment options are becoming available to manage left ventricle-related diseases. By staying informed and working with healthcare professionals, individuals can make informed decisions about their heart health and reduce their risk of left ventricle-related diseases.



