What Is Gallbladder Diet? Easy Meal Plans
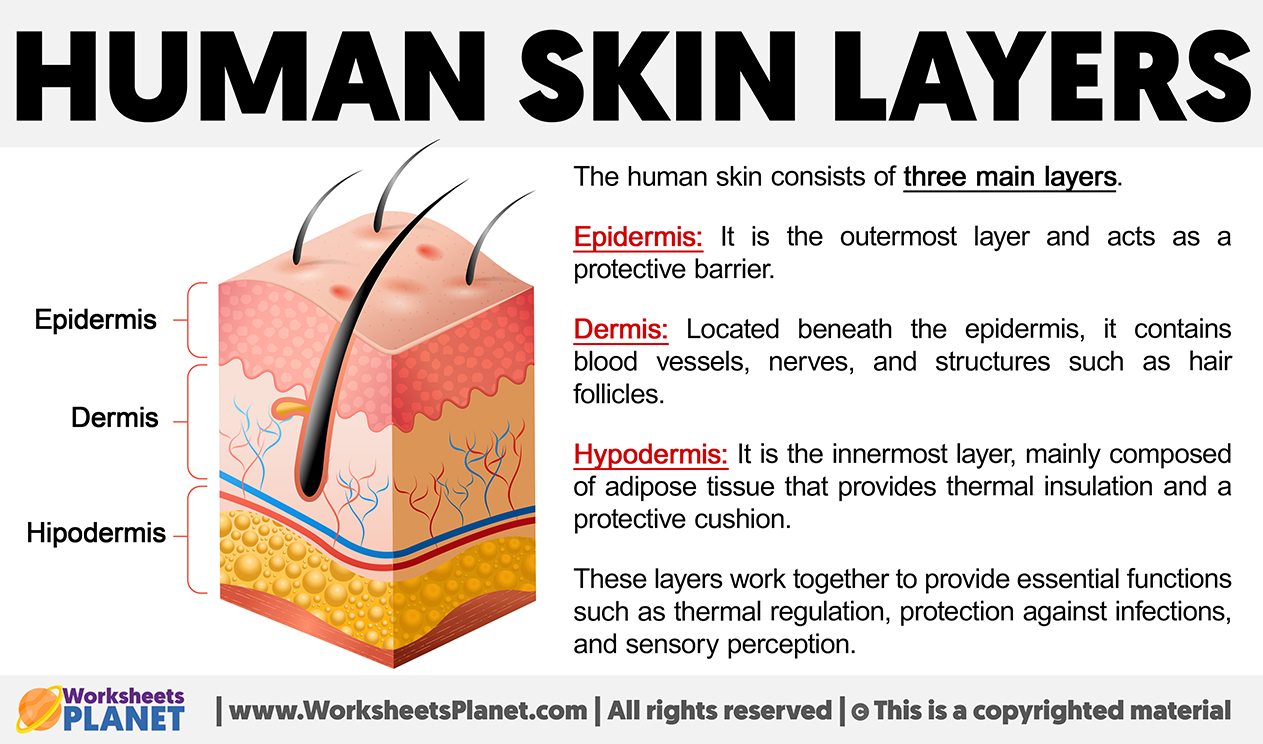
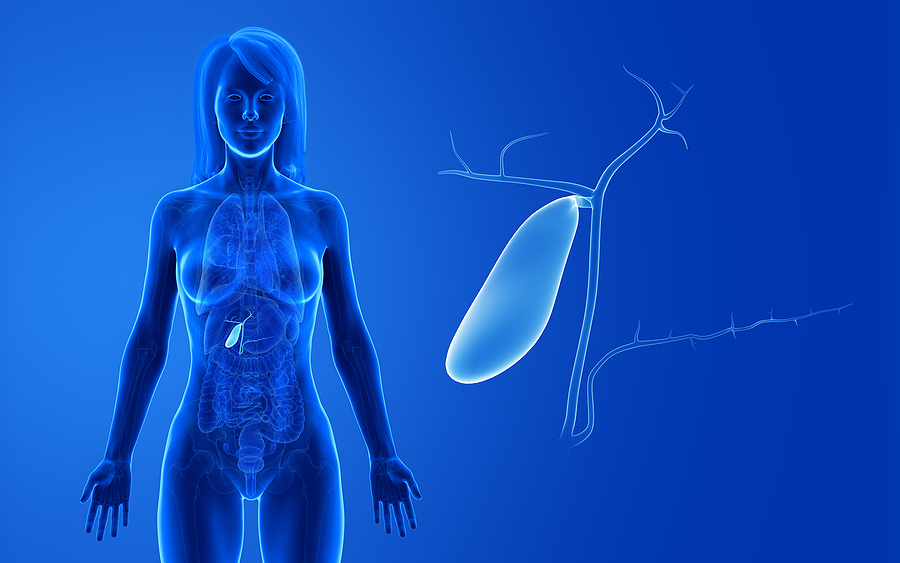
The gallbladder, a small, pear-shaped organ located under the liver, plays a crucial role in the digestive process by storing bile, a fluid produced by the liver that aids in the digestion and absorption of fats. A gallbladder diet is designed to support the health of this organ, particularly for individuals who have had their gallbladder removed (cholecystectomy) or are experiencing gallbladder issues such as gallstones. The primary goal of a gallbladder diet is to minimize symptoms and support overall digestive health through dietary adjustments.
Key Points
- A gallbladder diet focuses on reducing symptoms and supporting digestive health, especially for individuals with gallbladder issues or post-cholecystectomy.
- The diet typically includes foods that are easy to digest, low in fat, and high in fiber.
- Meal planning involves choosing the right foods, portion control, and eating smaller, more frequent meals to ease digestion.
- Hydration and limiting foods that can trigger gallbladder symptoms are also crucial components of the diet.
- Consulting with a healthcare provider or a dietitian is recommended to tailor the diet according to individual needs and health status.
Understanding the Gallbladder Diet

The gallbladder diet is not a weight loss diet but rather a therapeutic approach to managing gallbladder disease or its aftermath. It emphasizes foods that are gentle on the digestive system, thereby reducing the strain on the liver and the digestive tract. Key components of the gallbladder diet include foods that are low in fat, as high-fat foods can trigger gallbladder attacks in some individuals. It also includes a high intake of fiber, which can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of gallstones.
Foods to Include and Avoid
Foods that are recommended in a gallbladder diet include lean proteins like chicken, fish, and turkey, as well as low-fat dairy products. Fresh fruits and vegetables are also encouraged due to their high fiber and water content, which can help prevent constipation and reduce bile concentration, a factor in gallstone formation. Whole grains, such as brown rice, oats, and whole-wheat bread, provide essential fiber. Healthy fats like those found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil are beneficial in moderation. Foods to avoid or limit include fatty meats, full-fat dairy products, fried foods, and processed meats, as they can exacerbate gallbladder symptoms.
| Nutrient | Recommended Daily Intake | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber | 25-30 grams | Fruits, vegetables, whole grains |
| Protein | 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight | Lean meats, fish, poultry, legumes |
| Healthy Fats | 20-35% of total daily calories | Nuts, seeds, avocados, olive oil |
Creating Easy Meal Plans
Planning meals in advance can make adhering to a gallbladder diet easier and less overwhelming. Starting the day with a gentle breakfast, such as oatmeal with fruit or scrambled eggs with whole-grain toast, can set the tone for healthy eating throughout the day. Lunch and dinner should include a balance of lean proteins, vegetables, and whole grains. Snacking on fruits, nuts, and carrot sticks with hummus can help maintain energy levels and support digestive health.
Practical Tips for Meal Planning
Keeping a food diary can help identify which foods trigger symptoms, allowing for personalized adjustments to the diet. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is also crucial for digestive health and preventing gallstone formation. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can reduce the workload on the digestive system, potentially alleviating discomfort. Lastly, incorporating physical activity, such as walking, can aid in digestion and overall health.
What are the primary goals of a gallbladder diet?
+The primary goals are to minimize symptoms, support digestive health, and prevent the formation of gallstones through dietary adjustments.
Which foods should be avoided on a gallbladder diet?
+Foods high in fat, fried foods, processed meats, and full-fat dairy products should be limited or avoided as they can trigger gallbladder symptoms.
Is it necessary to consult a healthcare provider before starting a gallbladder diet?
+Yes, consulting with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian is highly recommended to tailor the diet according to individual needs and health status.
In conclusion, a gallbladder diet is a tailored approach to supporting digestive health, particularly for individuals dealing with gallbladder issues. By understanding the principles of the diet, including which foods to eat and avoid, and how to plan meals effectively, individuals can better manage their symptoms and support their overall health. Always remember, a personalized approach, guided by healthcare professionals, is key to achieving the best outcomes.